What is a blower motor?
-
Automotive
-
Automotive seat ventilation system

May 31, 2022
Blower motors are powered machines that create airflow using rotating blades. Similar devices include fans and compressors, and each is categorized based on discharge pressure/suction pressure ratios, with blower motors having a ratio of 1.11 to 1.20*. Blower motors are classified into four types: axial, diagonal, centrifugal, and cross flow.
*Definition by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
History of the blower motor
Historically, one of the very first blowers were the bellows used to supply air during iron smelting. These bellows are mentioned in literatures of ancient Rome and China. Bellows were at first manually operated, then underwent various enhancements over time such as the use of water power, evolving into an efficient means of air suppliment.
In more recent times, new power sources such as steam and electricity led to various developments of other pneumatic (air-driven) equipment. Some examples of applications are air brakes in steam locomotives or the opening and closing of automatic doors.
Nowadays, blowers and compressors are used in various industries, and are built into equipment such as transportation machines, processing or assembly, and packaging equipment. They are also found in products such as computers and home appliances, where they facilitate size reduction and performance enhancement.
Classification of blower motor types
Blower motors (blowers) are classified into four types: axial, diagonal, centrifugal (radial), and cross flow.
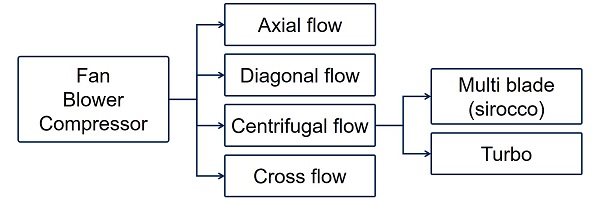
Axial flow
Axial flow types have blades that moves air parallel to the shaft on which the blades rotate. The axial flow blower can increase volume of air, and its efficiency is high even with a partial load. Due to its structure it is known to be noisy, and the disadvantage is that you can hear a jarring sound when you turn on the switch. This type of blower is used in a variety of applications, from small ones that are easy to disassemble and carry, to large ones that are extremely powerful.
Diagonal flow
In diagonal flow blowers, the impeller is inclined at a constant angle with respect to its axis of rotation, and air also flows in the same direction. Structurally, it has intermediate characteristics between the centrifugal type and axial flow type, and the operating principle is the same as that of the centrifugal flow type described in below.
Centrifugal flow
The centrifugal flow blowers use the centrifugal power supplied from the rotation of impellers to increase the kinetic energy of air. When the impellers rotate, the air near the impellers are thrown off from the impellers, then move into the casing. As a result, the kinetic energy of air is measured as pressure because of the resistance offered by the casing and duct. The air is then guided to the exit via outlet ducts. Centrifugal blowers generate more pressure for a given amount of air, used in various purposes such as leaf blowers, hair dryers, and climate control in air handling units. Centrifugal blowers can be classified into two types according to their structure: multi blade (sirocco) type and turbo type.
Multi blade (sirocco) type
The air flow is perpendicular to the axis of rotation, and the blades are typically angled forward in the direction of rotation. These types tend to be mid-range in terms of flow rate and pressure, and are used in applications such as duct ventilation, air conditioning, and cooling.
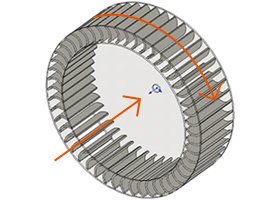
Turbo type
The air flow is perpendicular to the axis of rotation and the blades are typically angled backward with respect to the direction of rotation. These types tend to feature a low flow rate and high pressure, and are used in applications such as vacuum cleaners and dryers.
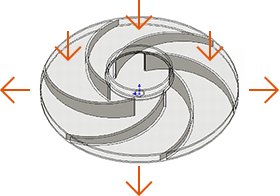
Cross flow
Cross flow blowers suck in air from one radial direction of the impeller and blows it from a radial direction of about 90 °. Air volume is even, and it is easy to lengthen the outlet while reducing the size, but its pressure cannot be high. Cross-flow blowers are widely used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC).
Applications of blower motors
A blower motor is mainly used for cooling devices and electrical equipment.
Example usages in commercial products
- Air intake
- Air intake at manufacturing plants where machinery such as presses or welding machines are used
- Suction
- Suction to hold objects in place at food, textile, and other such manufacturing plants
- Vacuum gripping
- Suction for vacuum packing vegetables or to hold and lift paper or other processing materials
- Transportation
- Transportation in equipment such as pneumatic tubes or powdered material transporters
- Dust extraction
- Dust extraction at manufacturing plants where grinding is performed or powdered materials are used
- Ventilation
- Ventilation at worksites, trains, clean rooms, etc.
- Air supply
- Supply of air to gas burners, incinerators, or medical equipment
- Blowing
- Blowing for pipe cleaning, sandblasting, etc.
- Aeration
- Aeration of septic tanks or oxygen supply to aquaculture ponds
- Drying or cooling
- Drying or cooling processing materials on a production line
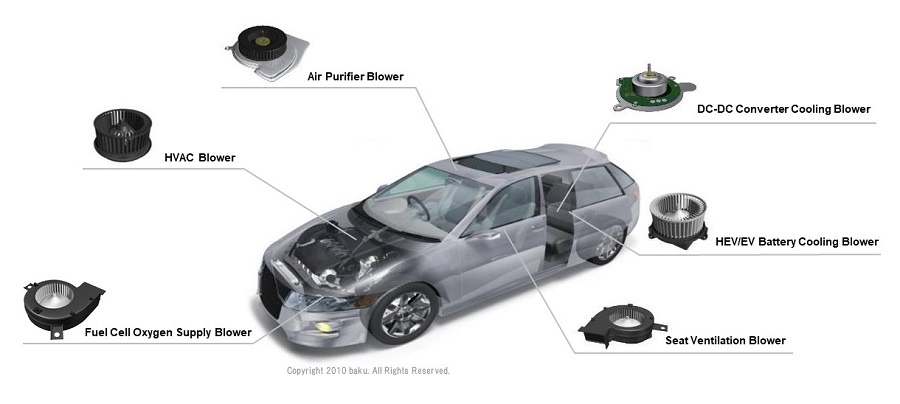
Example usages for automotive
- Seat heating/cooling blower
- DC-DC converter cooling blower
- HEV/EV battery cooling blower
- Fuel cell oxygen supply blower
- Air purifier blower
Overcoming your problems with ASPINA's advanced blower technology
The key to blower motor development is to study the electric motor, fan, casing, impeller, circuitry, and other components in detail to build up an accurate understanding of where performance losses occur. ASPINA draws on their expertise built up through many years of development, not only to optimize blowers or their motors to improve their performance, but also to make them smaller, lighter, have longer operating times. The vibration and noise level are reduced to low levels, using our accumulated manufacturing experience and know-how. Along with providing greater flexibility in product design, ASPINA’s blower motors can help reduce costs. ASPINA also has extensive scope for customization, so please don't hesitate to contact us.
If you have any questions or would like samples, quotations, consulting on customization etc., please feel free to contact us from our form.
Related information
-
Casing structure innovation provides quiet and comfortable driving experience – Automotive seat ventilation blower motor
Technologies

-
Compact and high performance seat ventilation systems made possible with back outlet blower motor
Case studies

-
Sleeve bearing development surpasses automotive industry standards – Automotive seat ventilation blower motor
Technologies

-
Accelerate product development: Rapid sampling and tailored solutions with ASPINA’s seat ventilation blowers
Case studies

-
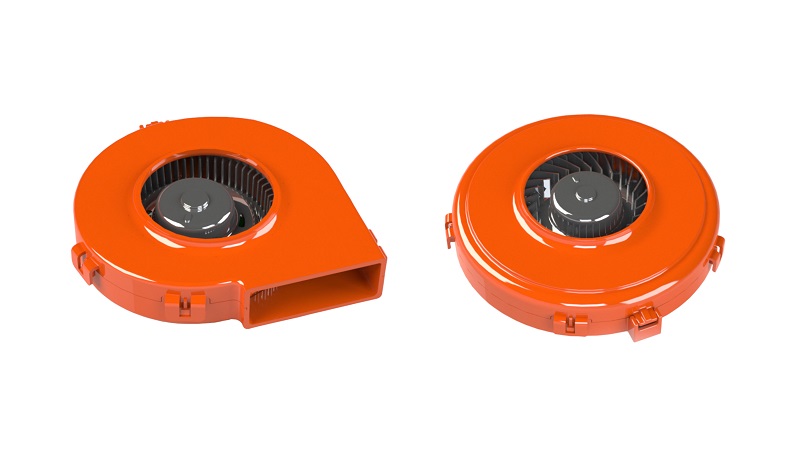
Seat ventilation blower
Products & services

-
HVAC blower motor
Products & services

List of the same series columns
- NEMA17 stepper motor selection guide: Mounting dimensions, applications, selection and problem solving
- NEMA stepper motor sizes chart and selection guide
- What does a stepper motor do?
- Applications for blower motor
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- Different types of DC motor and their respective features
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- Difference between brushed motor and brushless motor
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is a stepper motor?
- What is an actuator?
- How do brushless DC motors work? The need for a drive circuit explained
- What is an electric motor?
- What is a brushless DC motor?
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- How do brushed DC motors work? The need for regular maintenance explained
- How are stepper motors controlled? - Speed control of stepper motors
- How are DC motors controlled? - Speed control of DC motors
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
- What is a DC motor? - features and mechanisms
Related information
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others