Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
-
Automation
-
Health & wellness
-
Life environment
-
Automotive
-
Space
Jan. 27, 2021
Stepper motors can be found in many familiar home appliances, as well as in numerous domestic, commercial, and industrial applications. These applications leverage the stepper motor's ability to achieve precise positioning due to their feature of rotating in fixed intermittent steps.
This page provides an easy-to-understand introduction of the features, types, and applications for stepper motors.
Features and types of stepper motors
Stepper motors are driven by electrical pulses that determine their angle and speed of rotation. They are controlled by using a controller or oscillator that generates these pulses. The angle and speed of motor rotation are proportional to the number and rate of the input pulses respectively, so in other words, this simple drive mechanism can provide accurate control of motor position and speed.
Stepper motors can be grouped into three categories, VR, PM, and HB motors, depending on the structure of their rotor. They can also be further divided into unipolar and bipolar motors depending on the direction of current flow through their coil windings. As the different types of motors have different features, it is important to choose the right motor for the intended use.
Stepper motors offer the following advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Position control is very simple as the angle of rotation is proportional to the number of input pulses (digital input)
- Can rotate at low speed
- Open loop position control can be used, avoiding the need for feedback
- Remains securely locked in position when halted
Disadvantages
- Requires a drive circuit
- Prone to loss of synchronization when the load changes unexpectedly
- Generates high level of vibration and noise
For more information visit the following pages:
Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
How are stepper motors controlled? - Speed control of stepper motors
Home appliance and other domestic applications
Stepper motors are used in a wide variety of devices that take advantage of the accurate positioning made possible by their characteristic of rotating in fixed steps intermittently. Analog clocks are a familiar example, with the second hand of the clock being driven by a stepper motor that rotates in 6° increments, once every second. Other uses include operating air conditioning louvers, turning pipe valves on or off, driving electrically operated drapes, and the autofocus and zoom mechanisms in digital or phone cameras. Stepper motors are also used in home printers or the copier machines found at convenience stores.
Commercial applications
Stepper motors are also extensively used in commercial equipment encountered outside the home. Vending machines are one such application. In cup-filling vending machines, for example, a stepper motor operates the cup transport mechanism. In bank ATM machines, stepper motors drive the tray elevator and feed the paper through the receipt printer. At railway stations, they operate the feed mechanisms in ticket vending and validation machines, and drive the rotating security cameras that periodically reposition to surveil the surrounding area. These are just a few of the many applications where stepper motors are used.
Industrial applications
Although most of us will rarely come into contact with them in our daily lives, stepper motors also have uses in industry. Common examples include XY positioning tables or conveyor belt machines at production lines that need to advance at a constant rate. In applications such as conveyor mechanisms for transporting circuit boards, semiconductors, or other precision components, care needs to be taken to address the risk of vibration from the drive motor, as they can damage the components being transported. To prevent this, a micro-step drive can be used to minimize vibration from the stepper motor. This is one of the ways in which stepper motors help ensure the reliable conveyance of precision components.
Stepper motors are also used to drive the hands or joints of industrial robots. As greater precision and flexibility of movement can be achieved by attaching a rotary encoder to the stepper motor and performing servo control in the driver, it is anticipated that these motors will play an increasingly vital role in the field of robotics.
Stepper motors: An indispensable type of electric motor
Stepper motors rotate by a fixed angle each time a pulse is input to their driver circuit. These motors allow for simple open-loop position control as the angle of rotation is proportional to the number of input pulses. This capability is put to use in a wide variety of fields ranging from familiar devices such as home appliances, vending machines, railway ticket machines, and ATMs, to industrial equipment such as production lines and robots. In other words, stepper motors are indispensable to our way of life.
Overcoming your problems with stepper motors
ASPINA supplies not only standalone stepper motors, but also system products that incorporate drive and control systems as well as mechanical design. These are backed by comprehensive support that extends from prototyping to commercial production and after-sales service.
ASPINA can offer solutions that are tailored to suit the functions and performance demanded by a diverse range of industries, applications, and customer products, as well as your particular production arrangements.
ASPINA supports not only customers who already know their requirements or specifications, but also those who are facing problems at early stages of development.
Do you struggle with the following concerns?
Motor selection
- Don't have detailed specifications or design drawings yet, but need advice on motors?
- Don't have anyone in-house with expertise in motors and can't identify what sort of motor will work best for your new product?
Motor and associated component development
- Want to focus your resources on core technology, and outsource drive systems and motor development?
- Want to save the time and effort of redesigning existing mechanical components when replacing your motor?
Unique requirement
- Need a custom motor for your product, but been declined from your usual vendor?
- Can't find a motor that gives you the control you require, and about to give up hope?
Seeking answers to these problems? Contact ASPINA, we're here to help.
List of the same series columns
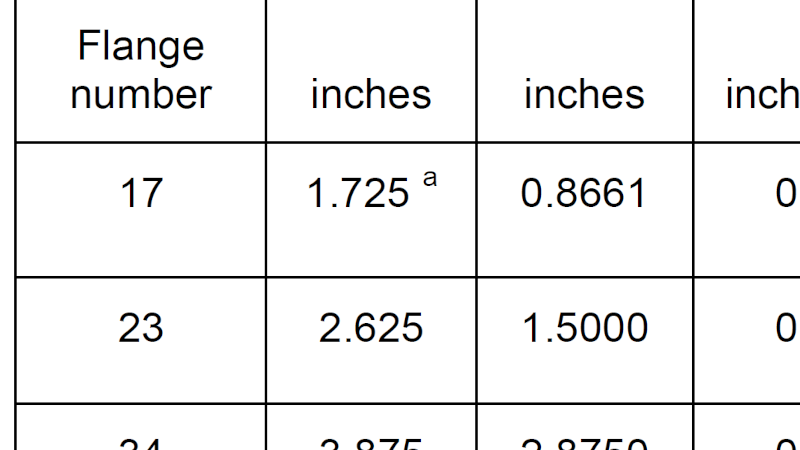
- NEMA17 stepper motor selection guide: Mounting dimensions, applications, selection and problem solving
- NEMA stepper motor sizes chart and selection guide
- What does a stepper motor do?
- Applications for blower motor
- What is a blower motor?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- Different types of DC motor and their respective features
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- Difference between brushed motor and brushless motor
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is a stepper motor?
- What is an actuator?
- How do brushless DC motors work? The need for a drive circuit explained
- What is an electric motor?
- What is a brushless DC motor?
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- How do brushed DC motors work? The need for regular maintenance explained
- How are stepper motors controlled? - Speed control of stepper motors
- How are DC motors controlled? - Speed control of DC motors
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
- What is a DC motor? - features and mechanisms
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others