What is a DC motor? - features and mechanisms
-
Automation
-
Health & wellness
-
Life environment
-
Automotive
Mar. 30, 2020
Generally, an electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, and uses the electricity generated to produce rotational motion and thereby to do work.
While there are many different types of motors, this page focuses on DC motors, which are electric motors driven by direct current (DC).
DC motors are used in a wide variety of different devices and appliances that play a part in our lives.
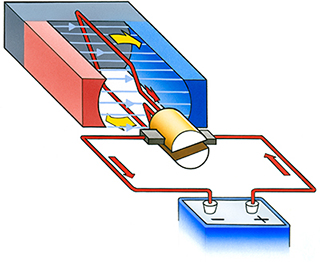
What distinguishes a DC motor from other types of electric motors?
Types of electric motors
The many different types of electronic motors can be broadly grouped into the following three categories based on their internal design and how they work.
- DC motors (powered by direct current)
- AC motors (powered by alternating current)
- Stepping motors (motors that rotate one step at a time in response to electrical pulses)
Two features that distinguish DC motors from the other two types are their high starting torque and ability to run at high speed.
Horizontal scrolling
| DC motor with brush | Brushless DC motor | AC motor | Stepper motor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Superior | Inferior | ||
| starting torque | Superior | Inferior | Inferior | |
| Rotational speed | Higher depending on setting | 3,600rpm or less (bipolar, 60Hz) |
2,000rpm or less |
|
| Possibility of Missing steps or slipperiness | No | slipperiness | Missing steps | |
| Long lifetime | Depending on lifetime of brush | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Need driver circuit | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Control algorithm applied | Normally closed loop | Normally open loop | ||
| Positioning control | Possible on servo motor | Possible on servo motor | Possible | |
| Constant speed control | Superior | Best | Inferior | Superior |
DC motors can be divided into brushed and brushless DC motors
DC motors are divided into two categories depending upon whether or not they use brushes and commutators.
Brushed DC motors work by direct connection to a source of DC electric power. Brushless DC motors, in contrast, require a drive circuit and work by supplying the appropriate current through static windings based on the detected orientation of the magnetic poles of the rotor.
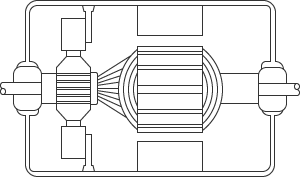 Cutaway schematic diagram of brushed DC motor
Cutaway schematic diagram of brushed DC motor
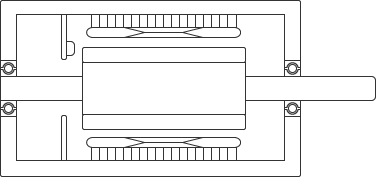 Cutaway schematic diagram of brushless DC motor
Cutaway schematic diagram of brushless DC motor
Respective features of brushed and brushless DC motors
Brushed DC motors
Brushed DC motors can be broadly divided into the following two types depending on whether they use permanent or electro-magnets.
- Permanent magnet brushed DC motor
- This is the most common form of electric motor used worldwide and includes the motors used in models and in the auxiliary motors of automobiles. They are further divided into slotted, slotless, and coreless motors depending on the configuration of the armature.
- Electromagnet brushed DC motor
- These types of motors use electromagnets to generate magnetic flux. They are further divided into distributed-winding, series-wound, and separately-excited motors depending on how the electrical connection between the field winding and armature winding is configured. This configuration is used for motors with medium to high output.
Brushless DC motors
Because their windings remain static, brushless DC motors do not require brushes and a commutator. They are divided into the following types based on how the permanent magnets are attached to the rotor.
- Surface permanent magnet (SPM)
- The permanent magnets are attached to the outer circumference of the rotor.
- Interior permanent magnet (IPM)
- The permanent magnets are embedded in the interior of the rotor.
Advantages and disadvantages of DC motors
Brushed DC motors are currently the most commonly used because they are easy to miniaturize and provide good control of rotation together with high efficiency.
Brushless DC motors, on the other hand, benefit from long life, ease of maintenance, and low noise because they do not have the brushes and commutators, which are the downsides of brushed DC motors.
Features of brushed DC motors
- Advantages
-
- No need for a drive circuit when running at constant speed
- High-efficiency design
- Able to operate at high speeds
- High startup torque
- Responsive and easy to use as speed and torque can be controlled by voltage
- Disadvantages
-
- Motor life is shortened by the need for brushes and a commutator, which are subject to wear.
- The brushes generate both electrical and acoustic noise
Features of brushless DC motors
- Advantages
-
- Lack of brushes means long motor life
- High-efficiency design
- Stability of speed control
- Able to operate at high speeds
- High startup torque
- Disadvantages
-
- A drive circuit is required
What are DC motors used for?
It is no exaggeration to say that DC motors are being used all around us in our daily lives. They are used in many different ways and take on many different forms. Examples from your home might include air conditioners, refrigerators, and water heaters. At work, DC motors will likely be used in your office's audiovisual projectors or inside the ATMs used by banks. Use of the motors extends well beyond these examples, encompassing home appliances, especially air ventilation systems, and also cars and medical devices.
DC motors are produced in huge volumes and, as a source of noise and a means of achieving energy efficiency, they play a very important role both in determining living conditions and in the global environment.
ASPINA supports customization of DC motors
"I am looking for a motor like this, ..."
"The other vendor told me it couldn't be done, ..."
ASPINA DC motors can be customized to suit a wide range of applications in different industries, including motors for prototypes, machinery, experimental apparatuses, and products produced in small lot sizes. We help to develop products in the best possible way by adapting to meet the customer's preferences for functions, performance, and production arrangements.
As a global supplier of electric motors, ASPINA is able to satisfy the diverse requirements of customers. By making full use of the design and development technologies we have acquired over time, we can find answers to even the most difficult problems and offer the best solutions.
We can customize DC motors to suit however you intend to use them and are open to inquiries for custom-made motors whatever they may involve, even one-off production. In response, we will deliver high-quality motors that match your needs.

List of the same series columns
- NEMA17 stepper motor selection guide: Mounting dimensions, applications, selection and problem solving
- NEMA stepper motor sizes chart and selection guide
- What does a stepper motor do?
- Applications for blower motor
- What is a blower motor?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- Different types of DC motor and their respective features
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- Difference between brushed motor and brushless motor
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is a stepper motor?
- What is an actuator?
- How do brushless DC motors work? The need for a drive circuit explained
- What is an electric motor?
- What is a brushless DC motor?
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- How do brushed DC motors work? The need for regular maintenance explained
- How are stepper motors controlled? - Speed control of stepper motors
- How are DC motors controlled? - Speed control of DC motors
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others