What is a medical device contract manufacturer?
-
Health & wellness

Mar. 7, 2025
A recent report indicates that the global medical device market was USD 518.46 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 886.80 billion by 2032*1. In the rapidly evolving field of medical technology, the role of medical device contract manufacturers is becoming increasingly important. These specialized companies provide a variety of services to ensure that medical device manufacturers can efficiently bring high-quality and compliant medical devices to the market. Join us as we examine the typical roles associated with medical device contract manufacturers and discover some of the tasks that our company engages in later in the article.
Please note that the technical terms mentioned in the text are explained in detail in the endnotes at the end of the page.
Role and key stages of medical device contract manufacturing
Medical device manufacturers are companies that design, produce, fabricate, assemble or process finished devices. Among them, medical device contract manufacturers perform contracted manufacturing activities (such as production, processing, packaging, storage and testing, either partially or fully) according to agreements with manufacturers. Additionally, the contracted tasks may include design improvements necessary for manufacturing. Whether design is included in the contract manufacturing process or not varies by country. In Japan, under the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Law (PMD Act), for instance, manufacturers are categorized by the operations they perform - design, main assembly, storage of final products and sterilization. In contrast, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States distinguishes between facilities that develop product specifications, referred to as specification developer, and medical device contract manufacturers.
Design and development
Medical device contract manufacturers take requirement specifications and design plans - created based on market and customer needs and expectations - as inputs to carry out design and development in compliance with regulatory requirements such as risk management*2, usability engineering*3, the software life cycle processes*4, cybersecurity*5 and safety standards*6. Verification and validation ensure that the medical devices meet all necessary requirements and are ready for mass production.
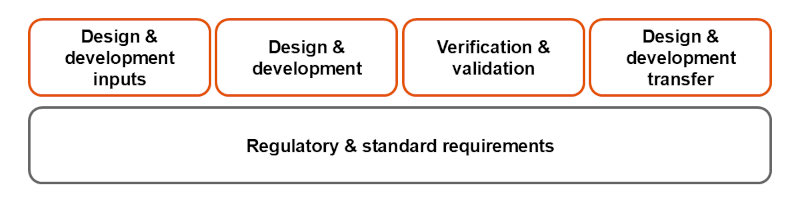 Concept diagram of design and development stage for medical device contract manufacturing
Concept diagram of design and development stage for medical device contract manufacturing
Production
Optimal process design and equipment design are conducted according to the type and quantity of medical devices. Through risk management, process validation*7 and software validation*8, appropriate manufacturing processes are realized. Additionally, to ensure the quality and safety of medical devices, appropriate production management is conducted from the selection and procurement of suppliers for purchased parts to the assembly, labeling, packaging and storage of final products. Production management includes:
- Identification and nonconformance management to prevent the market release of nonconforming and unfinished products and
- Traceability management, which includes various data necessary for impact analysis to determine correction and corrective actions for medical devices if nonconforming products are discovered in the market.
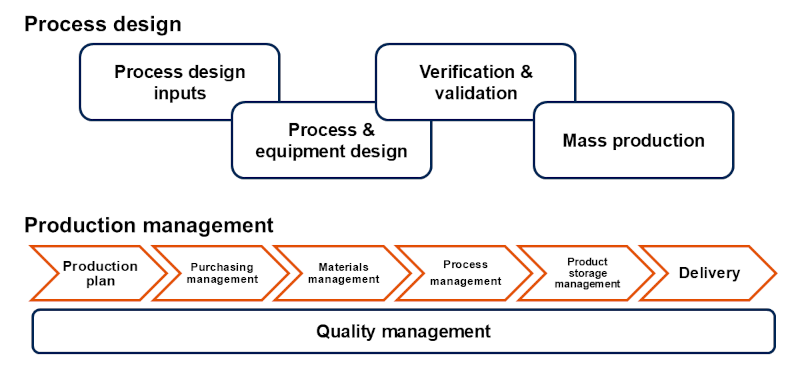 Concept diagram of production stage for medical device contract manufacturing
Concept diagram of production stage for medical device contract manufacturing
Product cleanliness and contamination control
Sterile medical devices have specific requirements, but even for regular medical devices, hygiene management such as product cleanliness and contamination control are necessary due to product characteristics. Contamination control has two aspects: managing contamination among workers handling the products and preventing the spread of contamination to the market. It is necessary to conduct production management and servicing activities with these aspects in mind.
Servicing activities
Servicing activities are strategic activities aimed at the support for continuous product use and improving customer satisfaction. In terms of support for continuous product use, medical device contract manufacturers provide installation, returns, repairs and service parts to maintain the quality and safety of medical devices in the market. For medical devices that require maintenance, maintenance services are offered. On the other hand, to improve customer satisfaction, technical advice and user training are provided.
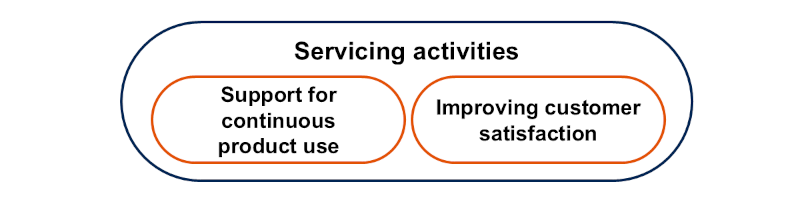 Concept diagram of servicing activities for medical device contract manufacturing
Concept diagram of servicing activities for medical device contract manufacturing
Compliance with regulatory requirements
One of the most crucial functions of medical device contract manufacturers is compliance with regulatory requirements. Various regulatory requirements exist in countries where medical devices are sold, such as the FDA in the United States, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) in Europe and the PMD Act in Japan. It is necessary to design and manufacture medical devices that comply with these regulatory standards.
ASPINA’s approach to medical device contract manufacturing
Design and development
We support numerous long-term partners across diverse markets where they have come to trust and rely on ASPINA’s design and manufacturing capabilities. We have been providing products for medical applications for over 40 years. This includes design and manufacturing components, module assemblies, and finished products such as pocket-type hearing aids for the Japanese market. ASPINA proactively develops engineering ideas to further enhance device performance, durability, and cost competitiveness.
Production
ASPINA has production bases in Japan, China and Mexico, promoting local procurement of parts based on effective supply chain management. Additionally, ASPINA purchases parts used in other fields such as automation, environment and automotive in bulk, enabling the provision of products with cost-effective parts procurement.
Servicing activities
ASPINA has a proven track record with pocket-type hearing aids in returns, repairs and service parts provision for medical devices in Japan, and can respond flexibly to consultation requests based on the content of the inquiries.
Compliance with regulatory requirements
ASPINA has registered with the authority for medical device manufacturing (design, main assembly, storage of final products) to manufacture medical devices for the Japanese market. Additionally, ASPINA has obtained the second-class marketing for medical devices and marketing and manufacturing certification of designated controlled medical devices for pocket-type hearing aids to manufacture and sell these devices in Japan. ASPINA has also acquired ISO 13485 certification, an international standard for the quality management system of medical devices, for the design and manufacture of some products in Japan, demonstrating experience in regulatory compliance. Currently, ASPINA is working on establishing systems that comply with FDA regulatory requirements and plans to expand these systems to production bases outside Japan in the future.
Reliable partner in medical device manufacturing - ASPINA
Medical device contract manufacturing companies are indispensable partners in the medical technology industry, offering comprehensive services that support the entire lifecycle of medical devices, from design and development to manufacturing, packaging and servicing. By leveraging ASPINA, medical device manufacturers can focus on technological innovations and deliver cutting-edge medical solutions to the market. ASPINA provides comprehensive support for manufacturers developing innovative, advanced medical devices. Please feel free to contact us if you experience any issues.
Related information
Endnotes
- *1 Global market data for medical devices
-
See “MEDICAL DEVICES INDUSTRY ANALYSIS” published by Fortune Business Insights
- *2 Risk management
- Risk is the combination of the probability of occurrence and the severity of harm (physical injury or health impairment, or damage to property or the environment). Throughout the life cycle of a medical device - from conceptual design, through development, purchasing, manufacturing and testing, to disposal - various foreseeable factors (such as misuse, dropping during transport or storage in high temperatures) that may cause the device to malfunction are considered. This includes both acceptable risks (low probability or severity, etc.) and unacceptable risks. By identifying risks throughout the lifecycle and taking preemptive measures for unacceptable risks, safe medical devices can be delivered to the market. This is one form of preventive action.
- *3 Usability engineering
- Usability engineering involves risk management to prevent medical errors caused by user mistakes. It focuses on the user perspective, ensuring that medical devices are designed for safe and effective use by their intended users.
- *4 Software life cycle processes
- Software life cycle processes are a set of processes for software development, which involves risk management to ensure software safety. It implements design processes and measures according to the degree of risk posed by foreseeable factors (such as sensor failures or accurate measurements are not possible under certain conditions) that may cause software modules to malfunction.
- *5 Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity involves risk management for protecting programs and data through measures that prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. It is closely linked to the software life cycle processes.
- *6 Safety standards
- Safety standards require that medical devices maintain their essential performance and safety even when exposed to external factors such as drops, impacts, electromagnetic interference or heat. Essential performance refers to the essential functions that must be maintained within anticipated external conditions and usage ranges (such as patient monitoring alarms, patient examination functions and drug delivery functions).
- *7 Process validation
- Process validation ensures that manufacturing processes and equipment operate according to specifications. It involves testing and confirming that the processes are capable of consistently producing products that meet predetermined quality criteria.
- *8 Software validation
- Software validation ensures that software used in quality management systems, manufacturing processes, and monitoring and measuring devices for medical devices performs its intended functions accurately. This involves testing and confirming these types of software's functionality and reliability.
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others