Comprehensive guide to medical device design
-
Health & wellness
-
CPAP
Sep. 24, 2024
Medical device design is a complex process that requires a thorough understanding of market needs, user requirements, regulatory compliance, and effective project management. These devices interact directly with human bodies intervening in biological activities, which makes their careful design critical to ensure they do not cause harm. Additionally, for design and manufacturing companies, achieving financial sustainability is essential. This requires balancing the investment in rigorous design and testing processes with efficient production methods to deliver safe, effective and market-competitive medical devices. To cope with the complex process of medical device design, medical device manufacturers often choose to work with OEM/ODM partners as one of the beneficial means of doing so, rather than on their own. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to help you navigate through the design process, ensuring that your final product is both safe and effective for healthcare providers and patients.
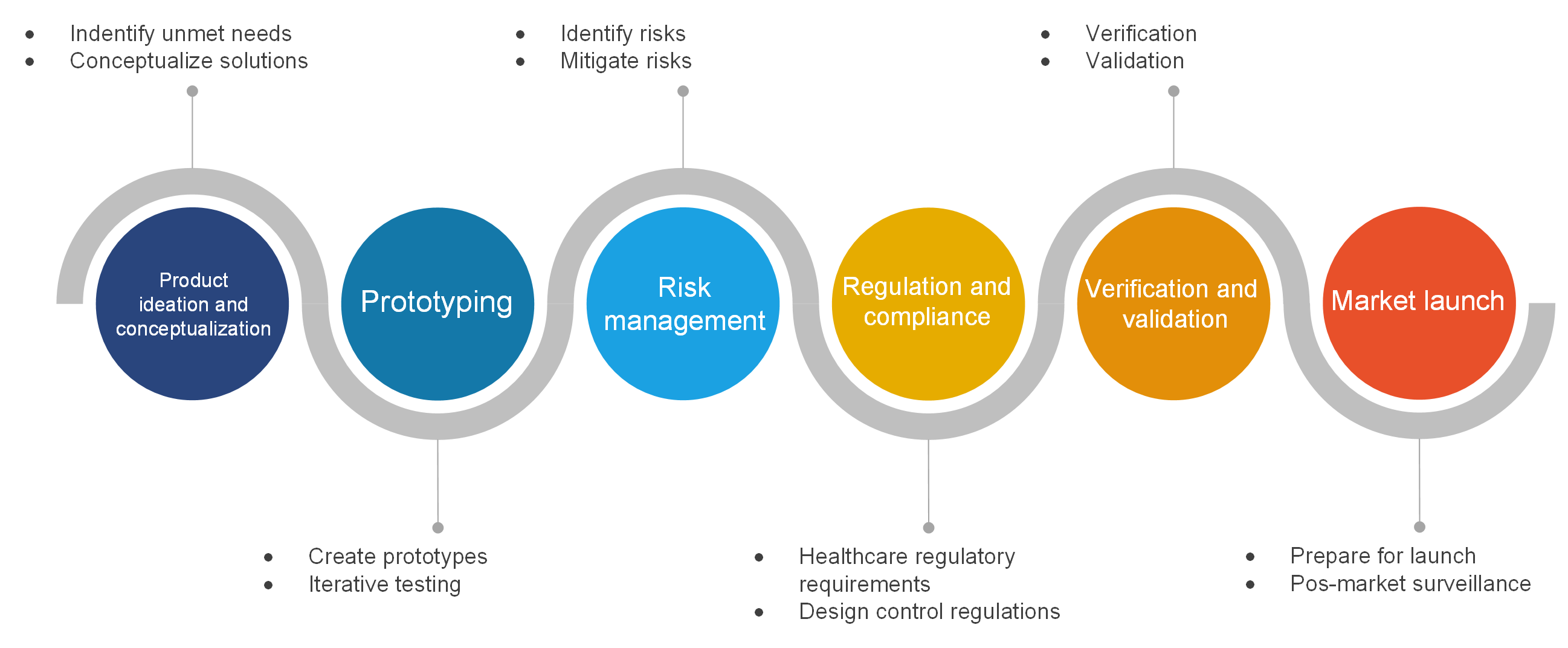 Medical device design process
Medical device design process
Step 1. Product ideation and conceptualization
Identify unmet needs
Start by researching and looking for gaps in the market. In doing so, it is useful to interview end-users such as doctors, nurses, and patients. Their perspectives are invaluable in designing medical devices, and through interviews, surveys and observations, gather detailed information on their needs, preferences and everyday challenges.
Conceptualize solutions
Once you have identified unmet needs, discuss with your team innovative solutions that can effectively address them. Devise several concepts and assess their feasibility and impact. In particular, feasibility should be thoroughly researched.
Step 2. Prototyping
Create prototypes
Develop prototypes of your medical device to test and refine the design. Prototyping allows you to identify issues early in the development process and make necessary adjustments before finalizing the design.
Iterative testing
Use an iterative approach to testing, where prototypes are continuously improved based on feedback and test results. This cycle of testing and refinement helps ensure that the final product meets all requirements and performs reliably.
Step 3. Risk management
Identify risks
Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential risks associated with your medical device. This includes analyzing all components and processes from various angles to identify potential problems.
Mitigate risks
Develop strategies to mitigate the identified risks. This can include design changes, additional testing, or implementing fail-safes. Effective risk management ensures that any potential hazards are addressed before they can affect end-users.
Step 4. Regulation and compliance
Healthcare regulatory requirements
Ensure that your design complies with all relevant healthcare regulations, such as those set by the FDA in the United States or CE marking in Europe. Understanding these regulations from the outset will help you avoid costly redesigns and ensure a smoother path to market.
Design control regulations
Implement robust design controls to manage the development process and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. This includes creating and maintaining documentation that demonstrates adherence to these controls throughout the development lifecycle.
Step 5. Verification and validation
Verification
Conduct rigorous testing to verify that the device meets all specified requirements. This involves testing each component and the system as a whole to ensure that each component functions as intended.
Validation
Validate that the device fulfills its intended use in real-world conditions. This means testing the device in the environment where it will be used to confirm its effectiveness and reliability.
Step 6. Market launch
Prepare for launch
Develop a comprehensive plan for bringing your medical device to market. This includes marketing strategies, distribution plans, and post-market surveillance preparations to monitor the device’s performance after launch.
Post-market surveillance
Continuously monitor the device’s performance in the market. Gather feedback from users and use this information to make future improvements and ensure the ongoing safety and effectiveness of the device.
By following these steps, you can ensure a thorough and compliant design process for medical devices, ultimately leading to safer and more effective products for healthcare providers and patients.
Medical device design with Biodesign approach
Biodesign is a methodology that combines bioengineering and design thinking to address the needs of patients and healthcare professionals.
Biodesign can provide significant inspiration for medical device design that meet the needs of healthcare providers and patient-oriented healthcare settings. Biodesign is a methodology for medical device development founded in 2001 by Dr Paul Yock and his colleagues at Stanford University, USA. The approach, which uses bioengineering and design thinking, focuses on the perspectives of patients and healthcare professionals and aims to solve real problems in the field of use.
Biodesign: The Future of Health Care | Stanford Mussallem Center for Biodesign | Stanford Medicine
ASPINA supports manufacturers in developing and designing medical devices that meet the needs of the field. For example, ASPINA's quiet compact blower was developed to be quiet enough not to disturb sleep and small enough to be used near the bedside, allowing patients using CPAP devices to continue treatment comfortably. ASPINA contributes to the development of medical devices that prioritize the perspectives of patients and healthcare professionals. If you have any further questions or need more details on any specific aspect, feel free to ask!
Related information
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others